پرونده:Free-living amebic infections.png
اندازهٔ این پیشنمایش: ۷۰۰ × ۶۰۰ پیکسل. کیفیتهای دیگر: ۲۸۰ × ۲۴۰ پیکسل | ۵۶۰ × ۴۸۰ پیکسل | ۸۹۶ × ۷۶۸ پیکسل | ۱٬۱۹۵ × ۱٬۰۲۴ پیکسل | ۱٬۳۶۵ × ۱٬۱۷۰ پیکسل.
پروندهٔ اصلی (۱٬۳۶۵ × ۱٬۱۷۰ پیکسل، اندازهٔ پرونده: ۷۱۵ کیلوبایت، نوع MIME پرونده: image/png)
تاریخچهٔ پرونده
روی تاریخ/زمانها کلیک کنید تا نسخهٔ مربوط به آن هنگام را ببینید.
| تاریخ/زمان | بندانگشتی | ابعاد | کاربر | توضیح | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| کنونی | ۲ فوریهٔ ۲۰۲۳، ساعت ۰۹:۲۴ |  | ۱٬۳۶۵ در ۱٬۱۷۰ (۷۱۵ کیلوبایت) | Materialscientist | https://answersingenesis.org/biology/microbiology/the-genesis-of-brain-eating-amoeba/ |
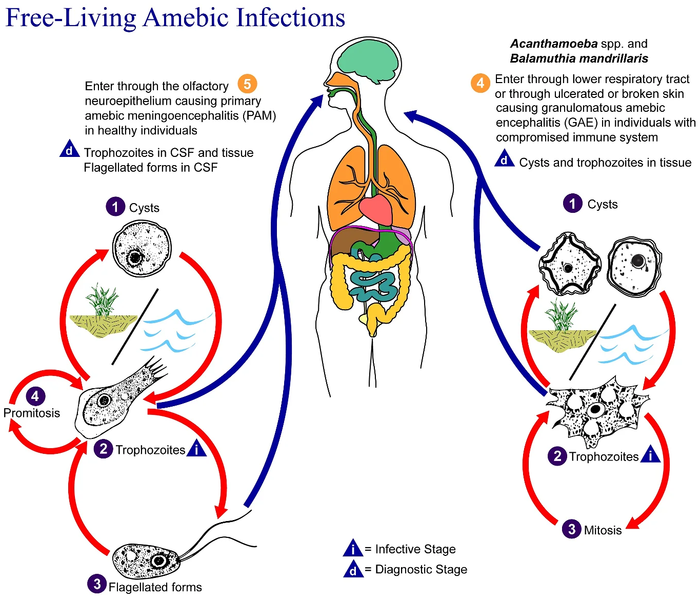
| ۲۰ ژوئیهٔ ۲۰۰۸، ساعت ۰۶:۳۰ |  | ۵۱۸ در ۴۳۵ (۳۱ کیلوبایت) | Optigan13 | {{Information |Description={{en|This is an illustration of the life cycle of the parasitic agents responsible for causing “free-living” amebic infections. For a complete description of the life cycle of these parasites, select the link below the image |
کاربرد پرونده
این پرونده در هیچ صفحهای به کار نرفته است.
کاربرد سراسری پرونده
ویکیهای دیگر زیر از این پرونده استفاده میکنند:
- کاربرد در de.wikibooks.org
- کاربرد در en.wiktionary.org
- کاربرد در fi.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در fr.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در gl.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در hr.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در is.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در it.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در pl.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در te.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در vi.wikipedia.org
- کاربرد در www.wikidata.org
- کاربرد در zh.wikipedia.org